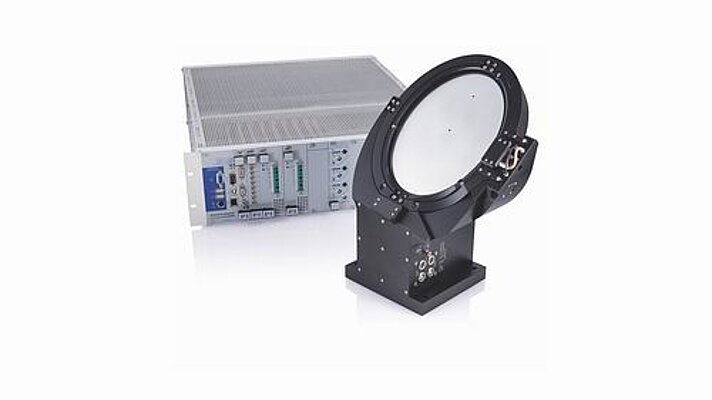
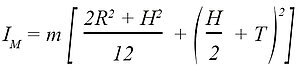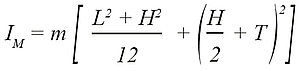PI's ultra fast steering mirror platforms and dither scanners are based on frictionless flexure guides and high-speed solid-state piezoelectric drives. A range of compact assemblies provide options from one to three axes of scanning. Multi axis scanners integrate pitch, roll and piston motion into one device with a single mirror or optic. They are faster than galvo-scanners and voice-coil driven beam steering systems (also available from PI) and can be used in both static and highly dynamic operation (e.g. scanning, tracking, image resolution enhancement, drift and vibration cancellation).
Applications include scanning, precision optical dithering, free-space optical communication (FSO), image stabilization, laser welding, semiconductor test & manufacturing, laser beam steering, astronomy, two photon polymerization, medical applications.
Read Article: Design, Performance, and Tuning of Fast Steering Mirrors based on Piezo Drives and Flexure Guides

Advantages of the PI steerable mirrors are: parallel kinematics design (coplanar multiaxis motion), fast response (sub-millisecond), high resolution (up to nanoradian range), long travel ranges (up to 3 degrees deflection). PI's parallel-kinematics multi-axis steering mirrors use only one platform/mirror for all axes. There is one common pivot point and no polarization rotation, an important feature for many precision optics applications.
Get Expert Advice and Tailored Quotes
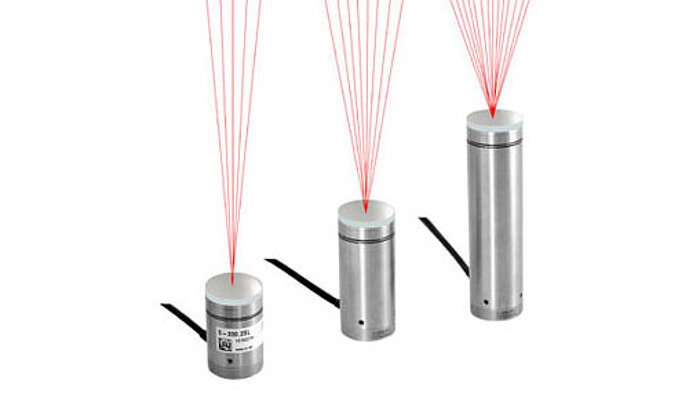
S-330 Fast Tip/Tilt Steering Mirror
Mirrors up to 50mm
- Fixed orthogonal axes with a common pivot point
- To 20mrad optical beam deflection
- Up to 20nrad resolution
- Closed-loop for high linearity

S-310/14 Z-Actuator – Phase Shifter
With Aperture
- 6/14µm piston motion
- Sub-millisecond dynamics
- Sub-nanometer resolution
- Open loop
- 10mm aperture
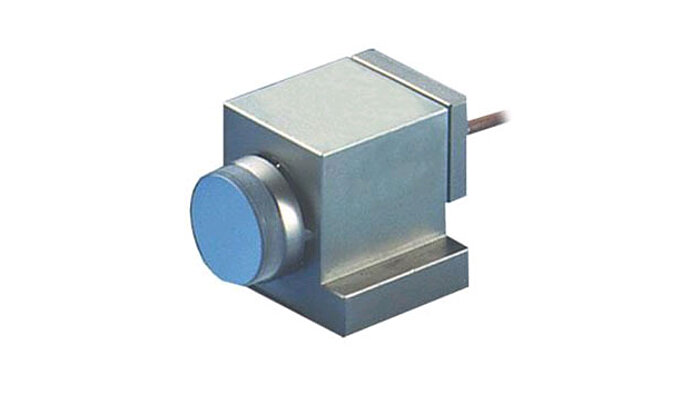
S-224 Fast Steering Mirror
Compact, 4mrad
- Sub-microradian resolution
- Sub-millisecond response
- 4.4mrad optical beam deflection
- Closed-loop option
- Includes BK7 mirror

S-331 Tip/Tilt Mirror Platform
High Dynamics, for ½” Mirrors
- 10mrad optical deflection
- High dynamics: 0.8msec rise time
- PKM: single pivot point
- Closed-loop for high linearity
- Up to 50nrad resolution

S-330 Fast Tip/Tilt Steering Mirror
Mirrors up to 50mm
- Fixed orthogonal axes with a common pivot point
- To 20mrad optical beam deflection
- Up to 20nrad resolution
- Closed-loop for high linearity

S-340 Fast Tip/Tilt Steering Mirror
Mirrors up to 100mm
- Fixed orthogonal axes with a common pivot point
- 4mrad optical beam deflection
- Sub-microrad resolution
- Closed-loop for high linearity

S-335 Tip/Tilt Mirror Platform
Long Travel, Mirrors up 1”
- 70mrad optical beam deflection
- Up to 100nrad resolution
- Closed-loop for high linearity
- PKM = Equal dynamics for both axes
- ID chip for auto calibrate

V-931 Fast Steering Mirror Platform
Voice-Coil Driven, Mirrors to 1”
- 140mrad (8°) optical deflection
- <1 µrad resolution
- Closed-loop voice coil drives
- PKM = Equal dynamics for both axes
- 20msec step response

N-480 Tip/Tilt Mirror Mount
Piezo Motors, 16° Tilt Angle
- Kinematic mount
- High stability PiezoMike motors
- For 0.5", 1" or 2" optics
- 1µrad resolution
- Vacuum versions to 10-9 hPa

Custom Example - Astronomy
Ultra-Stable, Piezo Mirror Mount
- ±2° tip / tilt range with PiezoWalk motor
- <0.5 arcsec angular resolution
- <1 arcsec position repeatability
- <20 arcsec static position stability
- >110Hz resonant frequency

Custom Example – Low Profile
Dynamic tip/tilt mirror (ΘXΘY)
- ±100µrad tip/tilt range
- Low profile design
Talk to our engineers about your custom steering mirror project.

S-325 Tip/Tilt Piston Mirror Platform
For 1” Mirrors
- Tripod design: pitch, roll, piston
- 10mrad optical beam deflection
- 30µm piston (Z-motion)
- Closed-loop for high linearity
- PKM = Equal dynamics for All axes

S-316 Tip/Tilt/Piston Platform
With 10mm Aperture
- Tripod design: pitch, roll, piston
- 2.4mrad optical beam deflection
- 12µm piston (Z-motion)
- Closed-loop for high linearity
- PKM = Equal dynamics for all axes

P-612 Piezo-Z Stage
Compact Z Stage, Aperture
- 100µm motion
- Compact: 60x60x27mm
- For cost-sensitive applications
- <1 nanometer resolution
- PICMA® long-life piezo drives

P-541 Piezo-Z & Z-Tip-Tilt Stages
Low-Profile, 80x80mm Aperture
- 100µm linear travel, 1 mrad tip/tilt
- Lowest profile: 16.5mm
- <1 nanometer resolution
- Choice of feedback sensors
- 80x80mm aperture

P-528 Piezo Z & Z/Tip/Tilt Stages
Parallel Metrology
- 50, 100, 200µm Z-motion
- Up to 4 milliradian Z/tip/tilt
- Precision trajectory control
- Sub-nanometer resolution
- Parallel capacitive metrology
PI offers a large range of fast steering mirrors (FSM) from compact systems for laser beam steering up to large units used for astronomy.
Single-Axis Tilt Platforms
The most compact approach is based on a flexure guided platform driven by a single actuator. For differentially driven platforms see “Tip/Tilt System with Differential Piezo Drive (Tetrapod) and improved Thermal Stability” below.
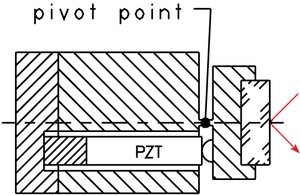
The platform is supported by one flexure and pushed by one linear piezo actuator. The flexure determines the pivot point and doubles as a preload for the Piezo actuator.
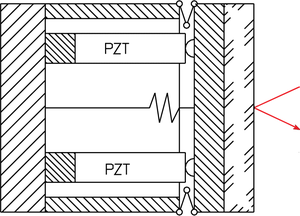
Single flexure, single piezo actuator (PZT) tilt mirror platform design. Advantages are the straightforward construction, compact dimensions and low costs. If thermal angular stability over a large temperature range is a critical issue, a differential piezo actuator drive system is recommended (see below).
Multi-Axis Piezo Steering Mirrors
Multi-axis piezo tip/tilt mirror platforms from PI are based on parallel kinematics with a single moving platform for all directions of motion. The common platform approach achieves higher linearity than can be attained by cascading single-axis mirrors in succession (e.g. with most galvo scanners). The single platform design also avoids polarization rotation and is much more compact than a multi-stage approach.
High Dynamics and High Stability
Piezo-actuated tip/tilt mirrors and platforms are suitable both for highly dynamic operation, such as tracking, scanning, image stabilization, elimination of drift and vibration, and for static positioning of optical systems and samples.
Direct Drive and Motion Amplified Steering Mirrors
Piezo steering mirrors can provide very fast response times in the sub-millisecond range and resolutions down to nano radians. Direct-driven units achieve higher dynamics, while designs that take advantage of on internal flexure motion amplifiers provide for larger optical beam deflection up to 100 mrad.
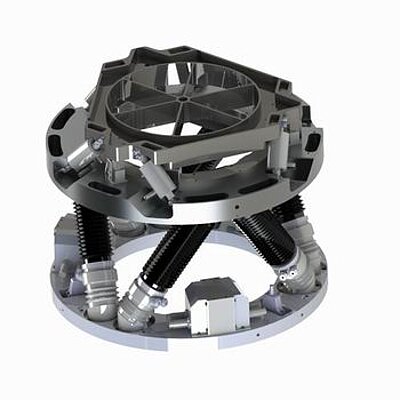
Tip/Tilt/Piston System - Tripod Piezo Drive
The platform is driven by three piezo actuators that are located in 120° angles to one another. By means of coordinate transformation, the motion can be split among the different actuators. In addition to tilting, the platform may also be used linearly in Z direction (piston motion), useful for phase shifting and correcting optical path length differences.
Tip/Tilt System with Differential Piezo Drive (Tetrapod) and improved Thermal Stability
The platform is driven by a total of four piezo actuators - two pairs with the θX and θY tilt axes arranged orthogonally removing the need for coordinate transformation. Each pair is controlled differentially, i.e. one actuator extends while the other one retracts by the same amount. The advantage of this approach is the improved thermal stability over a wider temperature range compared to a simpler, two actuator design. Just as the tripod, the differential version guarantees an optimum angular stability over a large temperature range. For position controlled versions, the differential evaluation of two sensors per axis provides an improved linearity and resolution.
Design principle of a differential piezo-actuator (PZT) steering mirror. This construction features two piezo linear actuators (operated in push/pull mode) per axis, supporting the platform. The case can be machined from one solid metal block with FEA (Finite Element Analysis) designed wire EDM (Electric Discharge Machining) cut flexures. The flexures provide for zero friction/stiction and excellent guiding accuracy. The differential design exhibits excellent angular stability over a wide temperature range - temperature changes only affect the vertical position of the platform (piston motion) and have no influence on the angular position. After the operating voltage is removed the platform returns to the center position.
Dynamics of Piezo Tip/Tilt Mirror Mechanisms
The dynamics and maximum operating frequency of a piezo tip/tilt system strongly depends on its mechanical stiffness and resonant frequency. The properties of amplifier, controller and closed-loop position sensor / circuit are also important. To estimate the effective resonant frequency of the system – a combination of platform and mirror – the moment of inertia of the mirror substrate needs to be calculated:
m = mirror weight [g]
IM = moment of inertia of a mirror [g × mm²]
L = mirror length orthogonally to tilt axis [mm]
H = mirror thickness [mm]
R = mirror radius [mm]
T = distance of pivot point to platform surface [mm]
The resonant frequency of the system is calculated with resonant frequency of the platform (see technical data) and moment of inertia of the mirror substrate using the following formula:
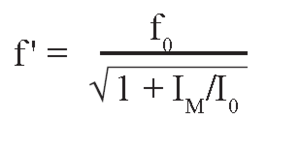
f' = resonant frequency of platform with mirror [Hz]
f0 = resonant frequency of platform without mirror [Hz]
I0 = moment of inertia of platform (see technical data) [g × mm²]
IM = moment of inertia of mirror [g × mm²]
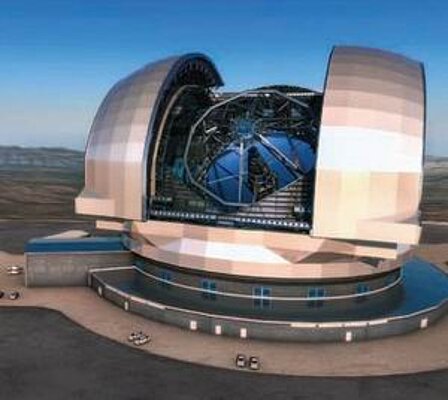
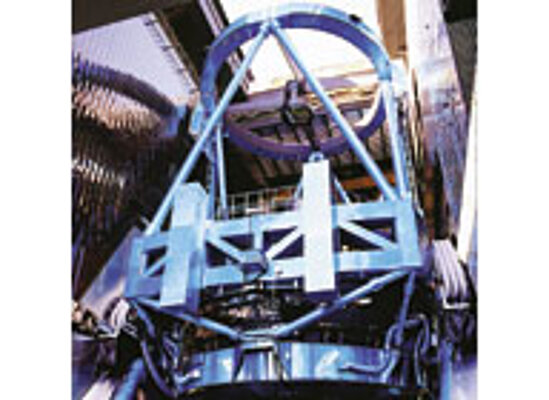
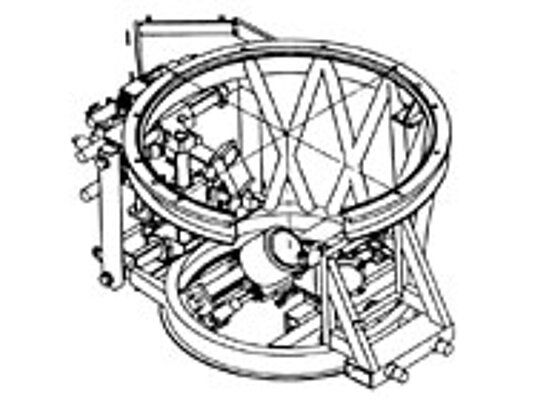
Hexapods and Fast Steering Mirrors / Active Optics in Astronomical Telescopes
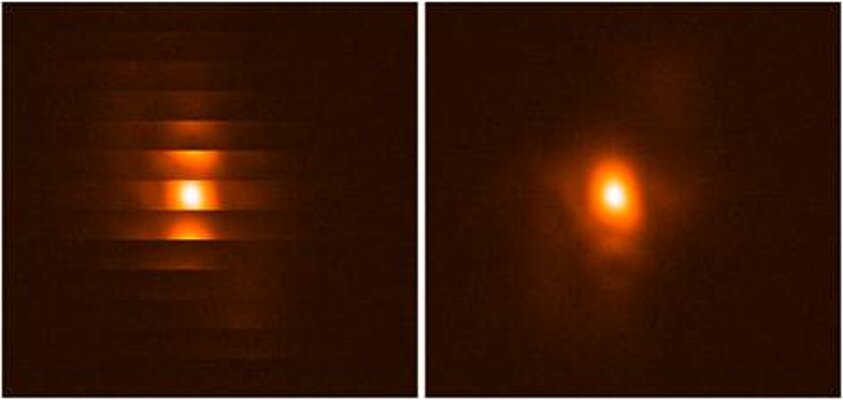
Resolution in large earthbound telescopes is limited by atmospheric turbulence and vibrations. During the last 35 years, PI has designed a number of large-aperture high bandwidth tip/tilt systems for image stabilization. Piezoelectrically driven active secondary mirrors can improve the effective resolution up to 1000% by correcting for these image shifts in real time, especially during long integrations with weak light sources.
Momentum Compensation
Due to the inertia of the large mirrors and the high accelerations required to correct for image fluctuations, significant forces can be induced in the telescope structure, causing unwanted vibrations. PI has developed momentum compensation systems integrated into the tip/tilt platforms which cancel undesirable vibrations and thus offer significantly better stabilization than uncompensated systems.
More Information on PI Precsion Motion Control Products in Astronomy
- PI wins Contract for Ultra-High Precision Positioning Actuators to Align Mirror Segments in the ELT Telescope
- Motorized Stages and S-330 Piezo Tip/Tilt in SOXS ESO Spectrograph Controlled by EtherCat Fieldbus
- P-845 Piezo Actuators / Control modeling of the fast-steering secondary mirror for GMT
- Ultra-Stable Mirror Mounts for LINC-NIRVANA High Resolution Imager


![Piezo actuator arrangement of a tripod Z/tip/tilt mechanism Piezo actuator arrangement of a tripod Z/tip/tilt mechanism. Tilt angles and piston motion (Z) are calculated with these formulas: θY = 2A-[(B+C)/2a]; θX = (B-C)/b; Z = (A+B+C)/3. A, B, C = linear displacement of the relevant piezo actuators.](/fileadmin/_processed_/f/0/csm_TripodSteeringMirror_7eec8005ea.png)